0. 前言
- 之前是Java后端工程师,写过不少代码。现在一方面好久没写Java了,一方面也想省力,所以就用了Flask。
- 参考资料:
- 安装:
- 安装flask:
pip install flask - 安装swagger:
pip install flask-restplus
- 安装flask:
1. 基本功能
- 需要注意的是,使用
flask-restplus后,设置路径、参数的方法与原始flask有所不同。 - 本文记录的都是
flask-restplus的功能。 - 需要实现的功能:
- 构建URL、设置静态文件(
1.1. 最简单的实例) - 设置请求方法(POST/GET/…)(
1.2. 设置请求方法) - 设置参数,包括URL参数和body内参数(
1.3. 设置参数)
- 构建URL、设置静态文件(
1.1. 最简单的实例
以下实例来自 Flask-RESTPlus 教程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13from flask import Flask
from flask_restplus import Resource, Api
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
class HelloWorld(Resource):
def get(self):
return {'hello': 'world'}
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)应用对象
Flask- 主要参数介绍:
import_name:应用名称。static_url_path:静态路径对应的URL,默认为static_folder的文件夹名,如果不为空则必须以/开头。static_folder:静态路径对应的文件夹,默认是static文件夹。static_path:deprecated,建议使用static_url_path替代。
- 静态文件获取主要通过上述几个参数。
- 对象定义:
1
2
3
4class flask.Flask(import_name,
static_path=None, static_url_path=None, static_folder='static',
template_folder='templates',
instance_path=None, instance_relative_config=False)
- 主要参数介绍:
应用运行
app.run()- 主要参数:
port,host,debug。 host设置访问权限,如果是127.0.0.1则只能本地访问,如果是0.0.0.0则服务器公开可用。- 调试模式(即
debug=True):使得程序修改及时生效。但对于Flask对象的修改不会及时生效。
- 主要参数:
构建url主要通过
api.route实现。
1.2. 设置请求方法
- 主要就是在
Resource类中新建对应的方法。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
class MyResource(Resource):
def get(self, id):
return {}
def post(self, id):
return {}
1.3. 设置参数
- url参数在
api.route中定义,可同时设置参数数据类型。- 参数类型默认是string,还可以设置为
int/float/string。
- 参数类型默认是string,还可以设置为
- 获取输入数据body中的json形式的参数。
- 通过
request对象获取,即request.json。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class CompareApis(Resource):
def get(self, source, category_name):
return {}
def post(self, source, category_name):
json_data = request.json
attr1 = json_data.get('attr1')
attr2 = json_data.get('attr2')
attr3 = json_data.get('attr3')
return {}
- 通过
2. 注解介绍
- 注解分类:
- 整个swagger页面的注解(
2.1. 基本对象 & 2.2. api.model 的使用) - 每一类接口的注解(
2.1. 基本对象 & 2.3. 每一类接口的注解) - 每个接口的注解(
2.1. 基本对象 & 2.4. 每个接口的注解) - 接口中每个参数的注解(
2.5. url参数注解)
- 整个swagger页面的注解(
2.1. 基本对象
Api对象- 主要参数
app:Flask对象version:版本,swagger显示内容之一。title:标题,swagger显示内容之一description:简单介绍,swagger显示内容之一contact:联系人,swagger显示内容之一doc:swagger页面地址,默认为/。default:默认namespace名称。
- 猜测:是不是应该把
Api对象也看作一个namespace? - 初始化定义以及对应注释
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53'''
The main entry point for the application.
You need to initialize it with a Flask Application: ::
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
Alternatively, you can use :meth:`init_app` to set the Flask application
after it has been constructed.
The endpoint parameter prefix all views and resources:
- The API root/documentation will be ``{endpoint}.root``
- A resource registered as 'resource' will be available as ``{endpoint}.resource``
:param flask.Flask|flask.Blueprint app: the Flask application object or a Blueprint
:param str version: The API version (used in Swagger documentation)
:param str title: The API title (used in Swagger documentation)
:param str description: The API description (used in Swagger documentation)
:param str terms_url: The API terms page URL (used in Swagger documentation)
:param str contact: A contact email for the API (used in Swagger documentation)
:param str license: The license associated to the API (used in Swagger documentation)
:param str license_url: The license page URL (used in Swagger documentation)
:param str endpoint: The API base endpoint (default to 'api).
:param str default: The default namespace base name (default to 'default')
:param str default_label: The default namespace label (used in Swagger documentation)
:param str default_mediatype: The default media type to return
:param bool validate: Whether or not the API should perform input payload validation.
:param bool ordered: Whether or not preserve order models and marshalling.
:param str doc: The documentation path. If set to a false value, documentation is disabled.
(Default to '/')
:param list decorators: Decorators to attach to every resource
:param bool catch_all_404s: Use :meth:`handle_error`
to handle 404 errors throughout your app
:param dict authorizations: A Swagger Authorizations declaration as dictionary
:param bool serve_challenge_on_401: Serve basic authentication challenge with 401
responses (default 'False')
:param FormatChecker format_checker: A jsonschema.FormatChecker object that is hooked into
the Model validator. A default or a custom FormatChecker can be provided (e.g., with custom
checkers), otherwise the default action is to not enforce any format validation.
'''
def __init__(self,
app=None,
version='1.0', title=None, description=None,
terms_url=None, license=None, license_url=None,
contact=None, contact_url=None, contact_email=None,
authorizations=None, security=None, doc='/', default_id=default_id,
default='default', default_label='Default namespace', validate=None,
tags=None, prefix='', ordered=False,
default_mediatype='application/json', decorators=None,
catch_all_404s=False, serve_challenge_on_401=False, format_checker=None,
**kwargs):
- 主要参数
namespace对象- 构建方法:
api.namespace() - 主要功能:
Group resources together,我的理解就是奖若干个接口放到一个组里一起显示。 - 主要参数:
name:名称description:swagger注解,每一类接口的简单说明。path:相关接口URL统一前缀,默认情况下为/{name},其中{name}就是第一个参数。
- 对应初始化函数以及对应注释。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15'''
Group resources together.
Namespace is to API what :class:`flask:flask.Blueprint` is for :class:`flask:flask.Flask`.
:param str name: The namespace name
:param str description: An optionale short description
:param str path: An optional prefix path. If not provided, prefix is ``/+name``
:param list decorators: A list of decorators to apply to each resources
:param bool validate: Whether or not to perform validation on this namespace
:param bool ordered: Whether or not to preserve order on models and marshalling
:param Api api: an optional API to attache to the namespace
'''
def __init__(self, name, description=None, path=None, decorators=None, validate=None,
authorizations=None, ordered=False, **kwargs):
- 构建方法:
2.2. api.model 的使用
对应文档:
作用:
- 构建接口输出的形式。
- 构建接口输入的形式。
整体思路:每个model拥有一个名称以及一个字典。
- 字典表示该model中属性的名称(key)以及对应的特征(value)。
- model可以嵌套使用。
构建注意事项:
- 构建方法:
api.model - 主要通过
flask_restplus.fields中各各类实现。 fields.Raw是所有类型对象的基类,包括的主要参数有:attribute:重命名属性default:默认值title:用于文档注解。description:说明,用于文档注解。required:bool,用于文档注解。readonly:bool,用于文档注解。
- 构建方法:
如何用于接口输入、输出的描述:
api.marshal_with(my_model, as_list=False):用于描述接口输出。可以设置as_list来表示输出的是一个序列。api.expect():用于描述接口的输入。如果要设置输入的为序列,则可以使用@api.expect[my_model]。
举例(仅关键代码)
- 构建了model。
- 将该模型作为输出、输出模型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24person = api.model('Person', {
'name': fields.String(
attribute="private_name",
default="John",
required=True,
readonly=True,
title="person_title",
description="person_description",
),
'age': fields.Integer,
})
school = api.model('School', {
'name': fields.String,
'students': fields.List(fields.Nested(person)),
'teachers': fields.List(fields.Nested(person)),
})
class MyResource(Resource):
def get(self, id):
return {}
上述实例对应的文档图片。
- 从图片上看,好像设置的那些参数,如
required,default等都不是特别清晰。 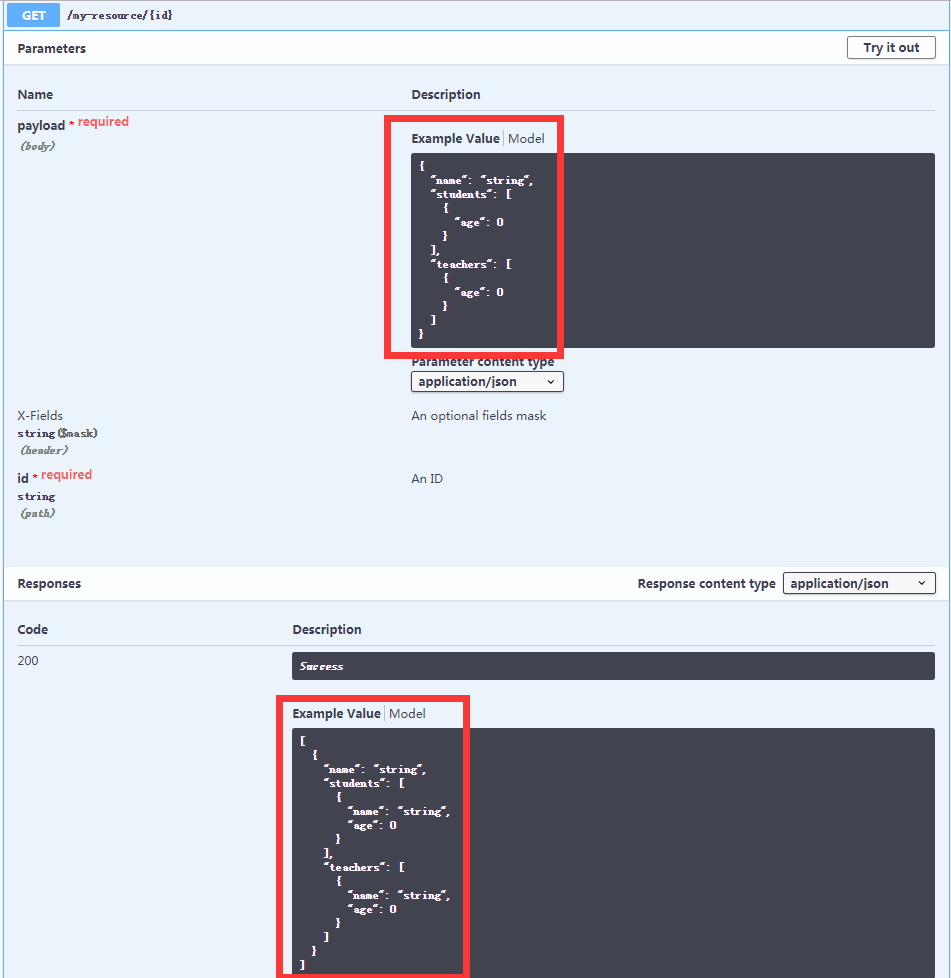
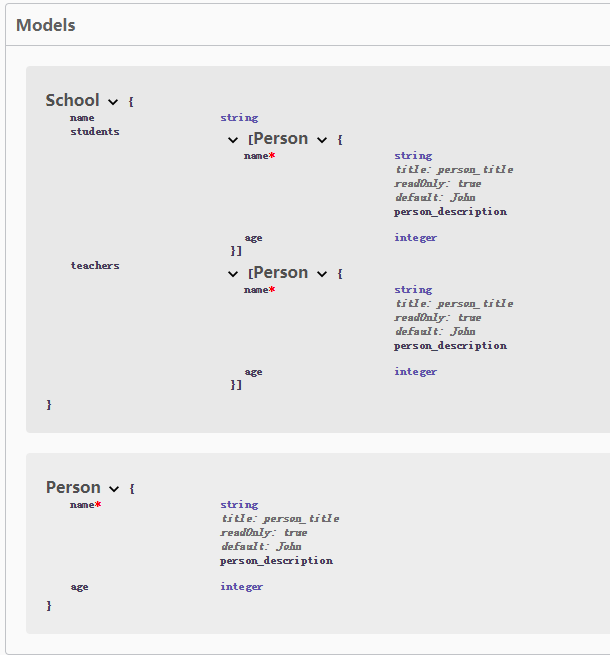
- 从图片上看,好像设置的那些参数,如
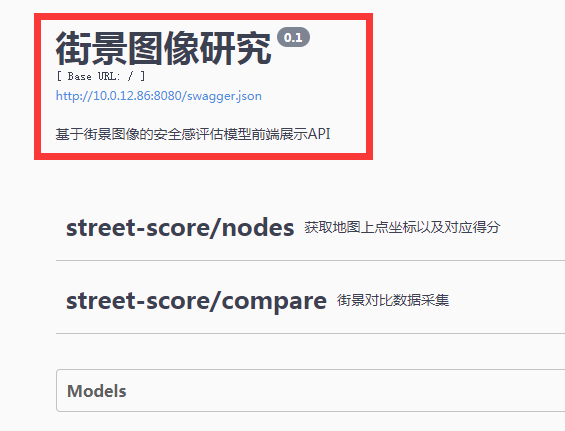
2.2. 整个swagger页面的注解
- 在初始化
Api对象时构建,具体查看2.1.对应内容。 - 效果如下图。
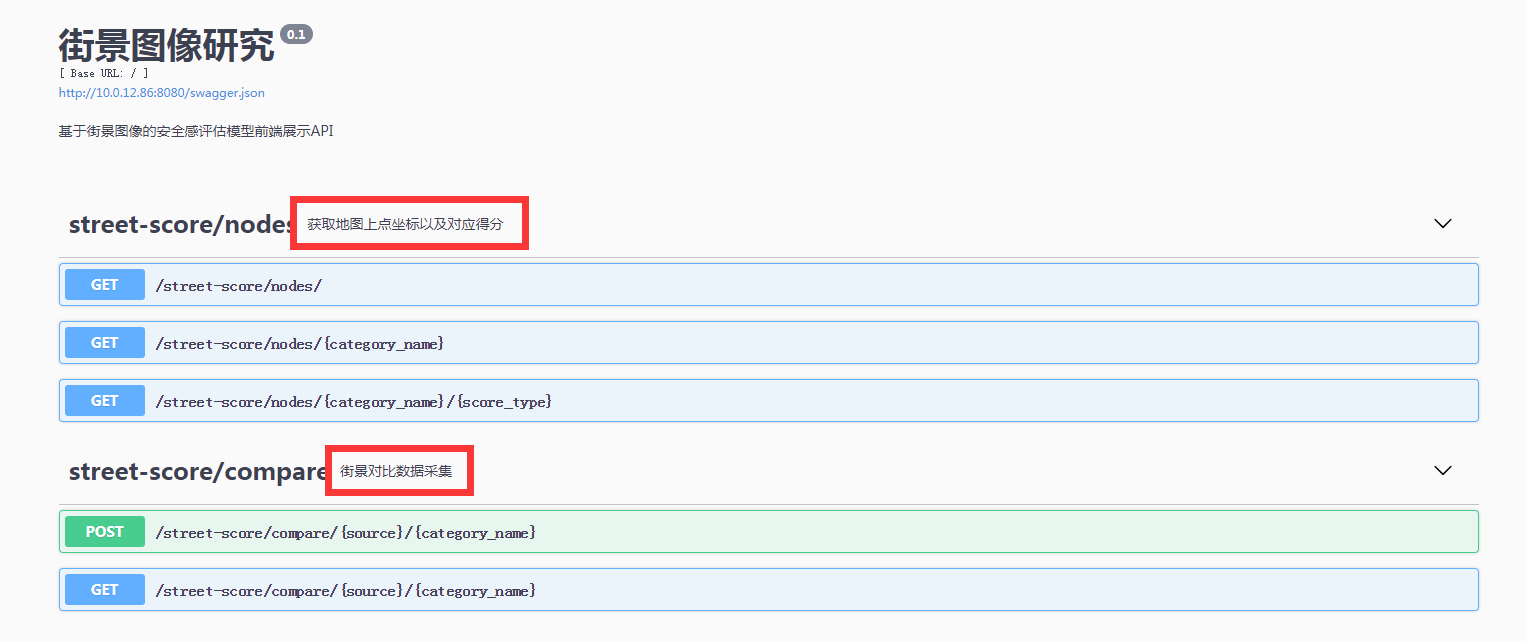
2.3. 每一类接口的注解
- 在初始化
namespace对象时构建。- 大概形式就是
api.namespace(name='', description="type in here")
- 大概形式就是
- 效果如下图。
2.4. 每个接口的注解
- 在定义URL的
route方法中构建。- 大概形式就是
@api.route('', doc={"description": "type in here"})
- 大概形式就是
- 效果如下图。

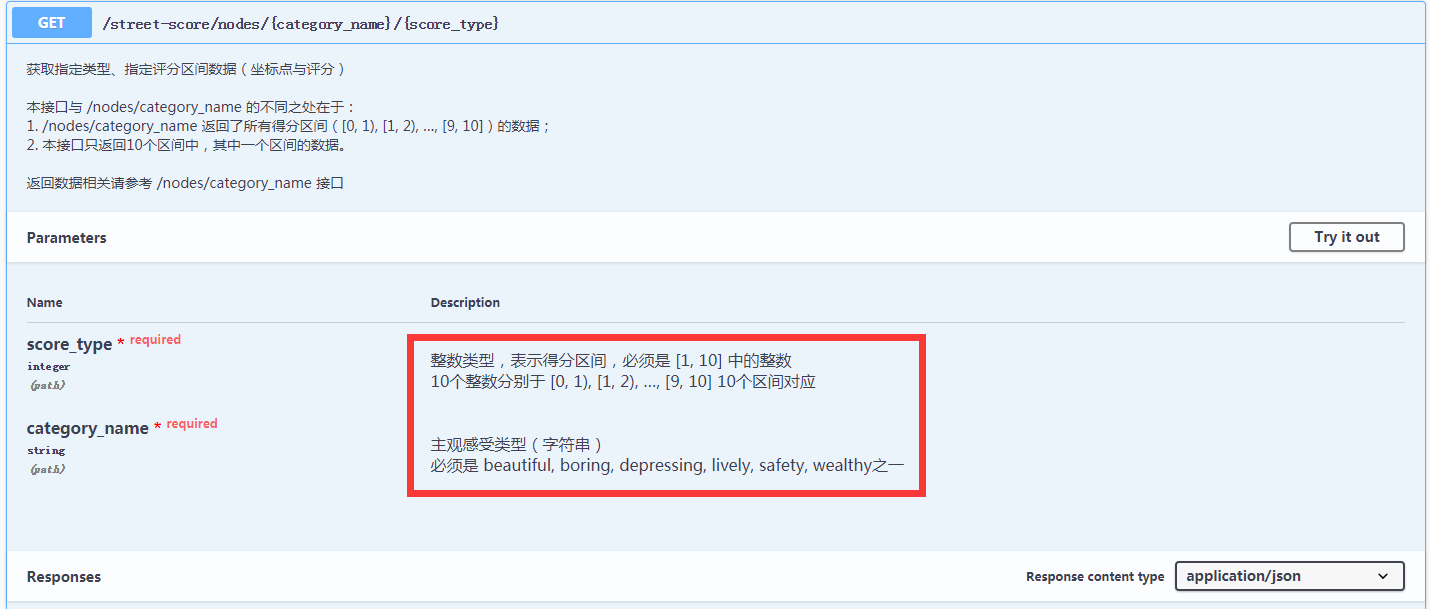
2.5. url参数注解
- 可使用
@api.doc(params={"id": "An ID", description="My resource"})注解对应class。 - 可使用多个
@api.param('id', 'An ID')注解对应class。 - 效果如下图。
3. 举例
1 | import sys |